https://seekingalpha.com/article/4682242-nuscale-power-shows-too-many-red-flags?mailingid=34945002&messageid=must_reads&serial=34945002.2465351&utm_campaign=email_mr%3Aevergreen_lp_premium_test_eligible_feb2024%2B2024-04-05&utm_content=seeking_alpha&utm_medium=email&utm_source=seeking_alpha&utm_term=must_reads_free_eligible
NuScale Power Shows Too Many Red Flags
Apr. 04, 2024 6:00 PM ET NuScale Power Corporation (SMR) Stock
Manuel Paul Dipold
Summary
- NuScale Power is a company working on small-scale nuclear reactors, but there are red flags including an unclear timeline, competition, and a CEO who sold all his shares.
- There are already functioning small modular reactors in Russia and China, with over 80 different designs worldwide, posing significant competition for NuScale.
- NuScale's cash reserves are low, and the company will need new liquidity soon, while the CEO's sale of all his shares raises concerns.
Investment thesis
NuScale Power (NYSE:SMR) is working on what appears to be an exciting product that will probably be in great demand in the future: small-scale nuclear reactors. The story is good, but a closer analysis reveals several red flags, such as an unclear timeline, a lot of competition, soon-to-be-depleted cash, and a CEO who recently sold 100% of his shares.
Company overview
NuScale's IPO was in May 2022 and is headquartered in Portland, Oregon. The company researches a new kind of nuclear power: small and modular. The company describes its "VOYGR" light-water reactors as "the future of nuclear" and says they are suitable for power generation, hydrogen production, or water desalination. According to the company, the system is designed to be modularly expandable and only needs to be refueled with new uranium every 24 months. The modular design offers many advantages: Locally flexible, easily transported by ship, train, or truck, and very safe (according to the company). Further advantages are also summarised in this article from the International Atomic Energy Agency:
Given their smaller footprint, SMRs can be sited on locations not suitable for larger nuclear power plants. Prefabricated units of SMRs can be manufactured and then shipped and installed on site, making them more affordable to build than large power reactors, which are often custom designed for a particular location, sometimes leading to construction delays. SMRs offer savings in cost and construction time, and they can be deployed incrementally to match increasing energy demand.
What are Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)? (IAEA)

Large, modular and micro reactors (IAEA)
Nuclear industry overview
Nuclear energy has experienced a revival in recent years. It is now clear and becoming increasingly clear to the politicians responsible that renewable energies alone will not be enough. They are too volatile, and storing the surplus energy is not easy or expensive. Therefore, a constant base of continuously generated energy is needed. Nuclear energy is the ideal solution in combination with the endeavor to reduce CO2 emissions. In addition, nuclear energy is comparatively very safe regarding direct and indirect fatalities.

According to Statista, around 60 new nuclear power plants are currently under construction worldwide.

The current state of SMRs
These are excellent prerequisites for small modular reactors. There is a general interest in nuclear energy, and its advantages are undisputed. If SMRs turn out to be more practical and cheaper to build or operate, these systems should have a golden future ahead of them.
However, many people are unaware of, and every interested reader of this article should know, that some SMRs are already in operation (in Russia and China), and many more are under construction or in planning. According to the IAEA, there are around 80 different designs worldwide. In other words, this area has massive competition, and some of the competition is already much more advanced than NuScale Power.
There are more than eighty (80) SMR designs under development and deployment at different stages in 18 Member States (...) The Akademik Lomonosov floating power unit in the Russian Federation with two-module KLT-40S was connected to the grid in December 2019 and started commercial operation in May 2020. The HTR-PM demonstrator in China was connected to the grid in December 2021 and is expected to reach full power operation by the end of 2022. The CAREM25 in Argentina is under construction and is expected to reach first criticality in 2026. The construction of ACP100 in China started in July 2021 and is targeted to start commercial operation by the end of 2026. The construction of BREST-OD-300 in Russian Federation began in June 2021 and is planned to be completed in 2026.
"Advances in Small Modular Reactor Technology Developments" (IAEA´s 420-page booklet)
In this document, on page 12, there is a list of various systems and the stages of planning or construction they are at. Many systems originate from Russia or China, but numerous US-based systems also exist. Although many are still in the design phase and not yet beyond that, it shows that there could be intense competition in this area, so small companies with limited cash could have a hard time. Here is an excerpt:

IAEA
In which phase are NuScale´s reactors?
According to this article from MIT Technology Review, the NuScale design for a reactor module that generates 50 MW of electricity has already been certified by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). But during the certification process, NuScale´s engineers changed the design again so that in the future a module will produce 77 MW instead of 50 MW. I added the bold text below.
“We found that we could actually produce more power with the same reactor, the same exact size,” says Jose Reyes, cofounder and chief technology officer at NuScale. Instead of 50 MW, the company found that each module could produce 77 MW. So the company changed course. For its first power plant, which will be built at the Idaho National Laboratory, NuScale is planning to package six of the higher-capacity reactors together, making the plant capacity 462 MW in total. The upgraded power rating requires some adjustments, but the module design is fundamentally the same. Still, it means that the company needed to resubmit updated plans to the NRC, which it did last month. It could take up to two years before the altered plans are approved by the agency and the company can move on to site approval, Reyes says.
We were promised smaller nuclear reactors. Where are they? (MIT)
The above article is from 2023, so it fits the timeline in the latest investor presentation; the company writes that the new design should be approved by July 2025. Overall, it is still a slowdown for the company.

To summarise, this means that the latest design has not yet been approved, and even if it is approved, this does not mean that it will go online quickly after that. It is not yet clear when the first modules will be ready to produce energy and generate revenue (after all, this is what investors are waiting for). The company has previously discussed the middle of this decade, but I can't find any dates in the latest documents. For me, this means that the company itself does not know; otherwise, this would be stated in the investor presentation.
NuScale´s numbers and financial trends
Total expenses are on an upward trend, while revenues are tiny at this point. In 2023, they generated $22.8M, which "arises from engineering and licensing services provided to potential customers" (10-K page 41). Additionally, in 2023, the company earned $10.8M interest on its cash.

In the latest Investor presentation, the company states that the net loss was $56.4M in Q4 2023. The cash position is about $125M, which means the remaining cash will only be sufficient for 2 or 3 more quarters.

The number of fully diluted shares is 262.8M * $5.5 (current share price) = $1.45B market cap.

As always, when there is no revenue but only the hope of a future business opportunity, it is tough to assess a valuation. Does the company deserve its $1.45B market cap? There is no clear yes or no answer to this question, but this is the figure that the current market attributes to the company. Therefore, this article focuses more on the general challenges and red flags that arise when analyzing the company. We are seeing that the market is slowly losing confidence in the company, and the stock is in a sustained downtrend, which is not surprising given the negative news, especially the issues I will mention in the next heading.

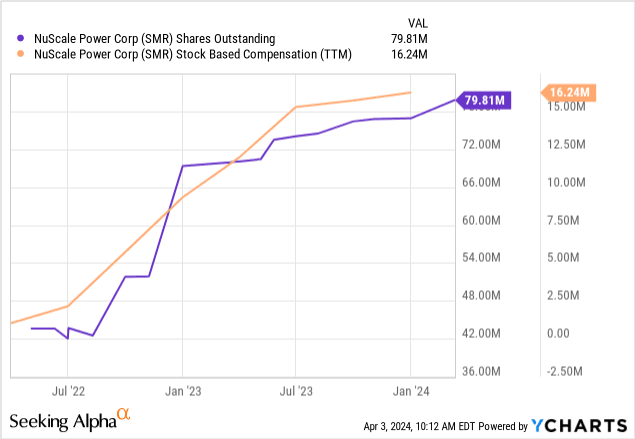
Share dilution, insider trades & SBCs
Given the above graphic about the fully diluted shares, we can see that only the Class A Shares are included below: those jumped in 2022 and continue to rise. Given the quarterly losses to date and the company's cash position, the company will need new liquidity quite soon, which could lead to more dilution for all existing shareholders.
These are all insider trades from the last six months. What stands out here is that the CEO, John L Hopkins, recently sold 100% of his shares. I have also not read any reports that he will soon give up his position as CEO or that there will be any other management changes. Of course, this sale could also have personal reasons that we are not aware of, but it is rare to see a CEO sell 100% of his shares.

openinsider
Conclusion
The analysis of this company reveals several red flags:
- The company's cash reserves are not particularly high, and the company will soon need new liquidity, so all indications are that the share dilution will continue
- The CEO has recently sold 100% of his shares
- The company gives no indication (at least not an obvious one) as to when the first system will be up and running, producing power and generating revenue
- The company states that business opportunities exist worldwide (Investor presentation page 5). A closer analysis shows that there are already functioning systems in several countries and massive competition in this area: there are more than 80 different SMR systems. I therefore doubt that these business opportunities exist worldwide: it is much more likely that NuScale will not be able to compete on price with the competition from Russia and China.
- The Q4 + full year 2023 presentation contains only 12 pages, and the latest general Investor presentation is only 22 pages. Also, the report in text form is very short. Overall, the potentials are discussed, as well as the need for clean energy and a growing energy demand. But there are not many hard facts with clear timelines.
- Overall, it is unclear how much potential there is on the market for small reactors and what long-term sales opportunities there are. These systems will still compete with larger nuclear reactors and renewable energy storage systems, which might become more and more attractive (due to falling prices) in the future. It is unclear if the combination of solar + storage might be cheaper in 2035. The point is, there are a lot of questions - too many for my taste.
So, what will happen to the share price? Given the almost unbroken downtrend of the past year and the many challenges this company seems to have, I think it will likely shed more of its $1.45B market capitalization. In my view, this is a shorting opportunity with an attractive risk/reward ratio.
Risks to my short thesis
There are general and company-specific risks to short-selling shares: Borrowing shares costs a percentage fee, which can be considerable, especially for smaller companies, and should be checked in advance. Theoretically, short-selling shares has infinite loss potential. Therefore, this stock market tool should be used very carefully and only if you are familiar with it. Regarding NuScale specifically, it could be that the future certification process goes faster than previously anticipated, which could lead to a sudden rise in the share price. Furthermore, it could be that the company achieves another technological breakthrough or wins a major contract from private companies or the government. A new partnership with another company would also be positive news for the company. Furthermore, the company has announced cost reduction measures to save $50M - $60M annually, which could lead to a lower cash burn and slower future share issuance.
All these possibilities could improve investor sentiment and lead to a sudden rise in the share price. Also, it should be noted that shares with a lower market capitalization are usually more volatile.
This article was written by
My focus is on a total return style with long and short positions (10-30% short positions). My main expertise is the current technological and geopolitical shift with the amazing investment opportunities they offer. Therefore, I always try to find stocks or whole sectors with favorable risk-reward structures. My long investment style is a core-satellite strategy: The core consists of large caps and/or ETFs. The satellites around this core are small caps, potential 10-baggers, and undervalued stocks. In short selling, I focus on overvalued stocks that will fall back down sooner or later. My name is Manuel Paul Dipold. Born in Germany but lived 8 years in Asia. I am myself an entrepreneur and have many entrepreneur friends. I am not a professional investor but it´s a hobby I love. So I know Europe and Asia very well and seek undervalued or high-growth stocks - always with valuation, geopolitical and social shifts in mind.
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, but may initiate a beneficial Short position through short-selling of the stock, or purchase of put options or similar derivatives in SMR over the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha's Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.